blue dot test testicular torsion|blue dot sign appendix testis : warehouse Testicular torsion classically presents with acute unilateral pain and swelling, abnormal cremasteric reflex, high position of the testicle, horizontal lie, and nausea/vomiting. WEBBrazzers – Jordi ENP & Ricky Spanish Go To Help Stunning Lily Starfire From Touching Herself. 158417 78%. Brazzers – Amber Alena Is Horny And Decides To Get Her BF’s .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da In the early 90s, Daniella Perez, one of the stars of the most successful soap opera in Brazil is brutally murdered by a fellow actor. Her mother, who took the investigation into .
torsion of testicular hydatid
interdatabase variability in cortical thickness measurements
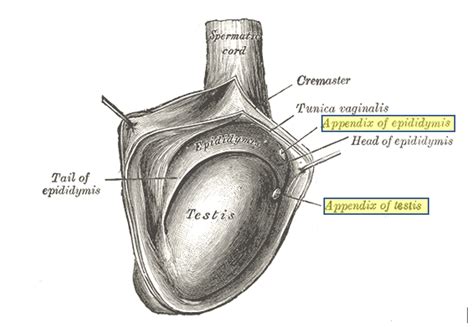
torsion of a testicular appendage
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding.Testicular pathologies that may mimic testicular torsion include torsion of testicular appendages, epididymo-orchitis, mumps orchitis, testicular infarct, polyorchidopathia, trauma, . During early onset, this may be differentiated from testicular torsion by maximal tenderness to palpation near the head of the epididymis or testis, an isolated tender nodule, .
When the appendix testis undergoes torsion, a hard, tender nodule may be palpable on the upper pole of the testicle, and a blue discoloration referred to as the “blue dot . Testicular torsion classically presents with acute unilateral pain and swelling, abnormal cremasteric reflex, high position of the testicle, horizontal lie, and nausea/vomiting. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency with a 4-6hrs window from the onset of symptoms to salvage the testis before significant ischaemic damage occurs. Any suspected case warrants urgent surgical exploration of .
Pathophysiology. Testicular torsion occurs when there is mechanical twisting of the spermatic cord, which suspends the testicle within the scrotum and contains the testicular artery and . Upon examination, a classic "blue-dot sign" (ie, a tender nodule with blue discoloration on the upper pole of the testis) may be seen; this finding on the upper scrotum is .
interference fringes in absorption measurements on thin films thickness
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and detorsion), it's likely to occur again. The more frequent the bouts of pain, the higher the risk of testicular damage. Family history of testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is the sudden twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. It most commonly affects neonates and young men. . (or blue discolored in venous engorgement), and tender hemiscrotum; Sudden, severe, unilateral scrotal pain in a patient with a tender, abnormally positioned testis on examination should be managed as . A neonatal boy is brought to his pediatrician for concern of a blue mass in the scrotum. His parents noticed this an hour ago. On physical exam, the scrotum is blue and firm with some erythema. Transillumination test is . Testicular appendage torsion Torsion of hydatid of Morgagni Torsion of the . The blue dot sign is a classic finding on physical examination which may be present. It describes a small firm nodule palpable at the superior aspect of the testis with bluish discoloration through the overlying skin.
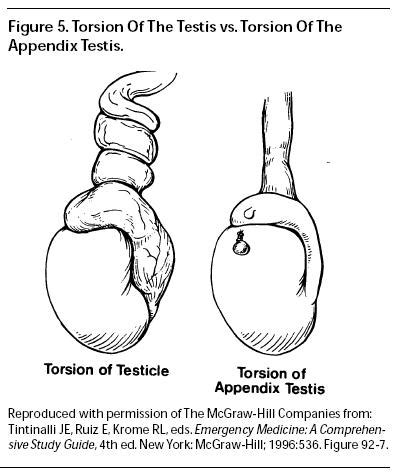
Conditions that may mimic testicular torsion, such as torsion of a testicular appendage, epididymitis, trauma, hernia, hydrocele, varicocele and Schönlein-Henoch purpura, generally do not .Classically, testicular torsion presents with sudden onset, severe scrotal pain with associated swelling, nausea and vomiting. 1,2,4,6,7 Importantly, however, this constellation of symptoms is not pathognomonic for testicular torsion and atypical presentations are also common. 3 Pain may arise several hours after vigorous physical activity or .Anatomy of the normal testis, bell clapper anomaly and intravaginal testicular torsion. Blue testis, Green epididymis, Lavender spermatic cord and vessels, Red tunica vaginalis. Normally, the epididymis extends along the full length of the testis posterolaterally so that the upper and lower poles of the testis are covered and the tunica vaginalis parietal lamina is anchored to the .
Testicular torsion is an emergency. It requires immediate referral to a surgeon . Red/blue Dark in neonate-Blue dot sign. Red. Bruising (consider causes, eg NAI) Cremasteric reflex . Usually absent . Usually present. Usually present . Usually present . Usually present . Reactive hydrocele. Possible. No. No. Possible. Possible .
The blue dot sign, a bluish discoloration of the skin of the superior pole of the scrotum, is considered pathognomonic for torsion of the testicular appendage but is uncommonly observed. 13 .
Testicular appendage torsion is the twisting of a small piece of tissue above a testicle. The appendage doesn't have a function in the body. . A blue dot at the top of the scrotum, which shows that the twist is in the appendage, not the testicle How is testicular appendage torsion diagnosed? . Urine test. This is to check for other possible .
Torsion of an appendage occurs when this tissue twists. Since this structure has no function, it does not pose any threat to your child’s health. . examination of the scrotum reveals what looks like a small “blue dot.” This is the swollen, dying appendage of the testicle. Contact the Division of Urology. Learn more about the Division of .
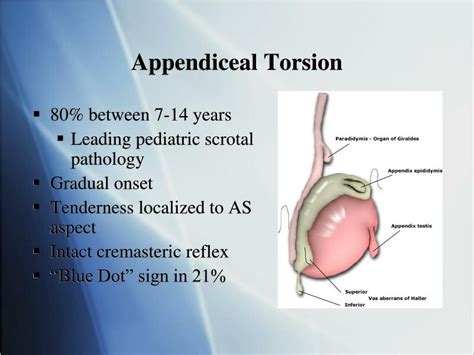
A blue dot visible on the scrotum, due to blood loss to the piece of tissue. Redness. . Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that must be treated to prevent testicle amputation. Care. How do you care for a torsed testicular appendix? If you or your child is diagnosed with appendix testis torsion, treatment will involve: Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous blood outflow, which can ultimately lead to necrosis or death of the testicular tissue.torsion and may be diagnosed by the “blue dot sign” (i.e., tender nodule with blue discoloration on the upper pole of the testis). Epididymitis/orchitis is much less common in the prepubertal In order to best see the blue dot sign, the skin must be stretched over the upper pole of the testis. However, the blue dot sign is only present in 10 to 23% of patients. 1 In cases that are equivocal, Doppler US can be used to rule out testicular torsion. 3. Management of torsion of the appendix testis is supportive with the use of NSAIDs .
The “blue dot” sign, a bluish discoloration in the area of the appendix testis, may be present on the scrotal wall, indicating infarction and necrosis. . If testicular torsion is clinically .
An absent cremasteric reflex is suggestive of testicular torsion (odds ratio = 7.8), whereas the reflex is preserved with epididymitis. 10 – 12 Torsion of the appendix testis is classically . Testicular appendage torsion Torsion of hydatid of Morgagni Torsion of the . The blue dot sign is a classic finding on physical examination which may be present. It describes a small firm nodule palpable at the superior aspect of the testis with bluish discoloration through the overlying skin.Question: What diagnosis is the blue dot sign associated with?Testicular torsionEpididymitisAppendicitisTorsion of the testicular appendageNephrolithiasis
Testicular torsion vs. torsion of testicular appendage. . A blue dot sign is considered pathognomonic, although very rarely clinically seen. This is an area less than 3mm with a pale bluish discoloration present on the scrotum at the superior pole caused by the cyanotic appendage beneath the scrotal wall. . Now test your knowledge with a .Testicular torsion presents with the rapid onset of severe testicular pain and swelling (Figure 3). . as this test is the single most useful adjunct to the history and physical . it can usually be seen through the skin and represents the "blue-dot sign." Doppler ultrasound will demonstrate a normally perfused testis, often with
Milder and more gradual onset compared to testicular torsion; Localized to one point of testicle; Physical exam Hard, tender 2-3mm nodule at upper pole of testicle; Transillumination: ischemic appendage appears as blue dot (highly sp, not sn) Differential Diagnosis Testicular Diagnoses. Scrotal cellulitis; Epididymitis; Fournier gangrene .
The characteristic blue dot is due to the cyanotic torsed appendage. The testicular appendage tends to calcify and degenerate over two weeks, and typically, no surgical intervention is required. . Ultrasound is not a perfect test for testicular torsion, especially in the very young. For example, 40% of neonatal testicles may have no apparent .
Epididymitis; Hernia; Trauma; Tumor torsion; Commonest causes: Responsible for 0.5% of total ED visits.; 85-90% cases: Appendage torsion + Testicular torsion + Acute epididymitis 75% cases: Testicular torsion + Acute epididymitis 25% cases: Testicular torsion (1:4000 males; peak age ~14 yrs) M/C cause: Acute epididymitis Special signs and Techniques
[1,2] Testicular torsion is a urological emergency that affects any age group but most common in the second and third decades of life. Pentyala et al. [6] reported a peak age range of 12-18 years . While a "blue-dot" finding is considered pathognomonic of a torsed testicular appendage, it is present in approximately 20% of patients. The combination of a "blue-dot" sign, along with the ability to palpate a non-tender testis underneath, can effectively make the diagnosis of torsion of the testicular appendage. Pediatric testicular torsion is an acute vascular event in which the spermatic cord becomes twisted on its axis (see the image below), so that the blood flow to or from the testicle becomes impeded. . a classic "blue-dot sign" (ie, a tender nodule with blue discoloration on the upper pole of the testis) may be seen; this finding on the upper .
Quatro anos após a destruição da Ilha Nublar, os dinossauro.
blue dot test testicular torsion|blue dot sign appendix testis